티스토리 뷰
Dev/React
20210613 React12 : Life Cycle 도표 이해하기, Reconciliation, Render 최적화 하기, react의 같은 component 인식, key Prop, shouldComponentUpdate, PureComponent, 함수를 prop으로 전달시 주의, Function Component render 제어(React...
라쿤 2021. 6. 14. 00:21React 12

Life Cycle 도표

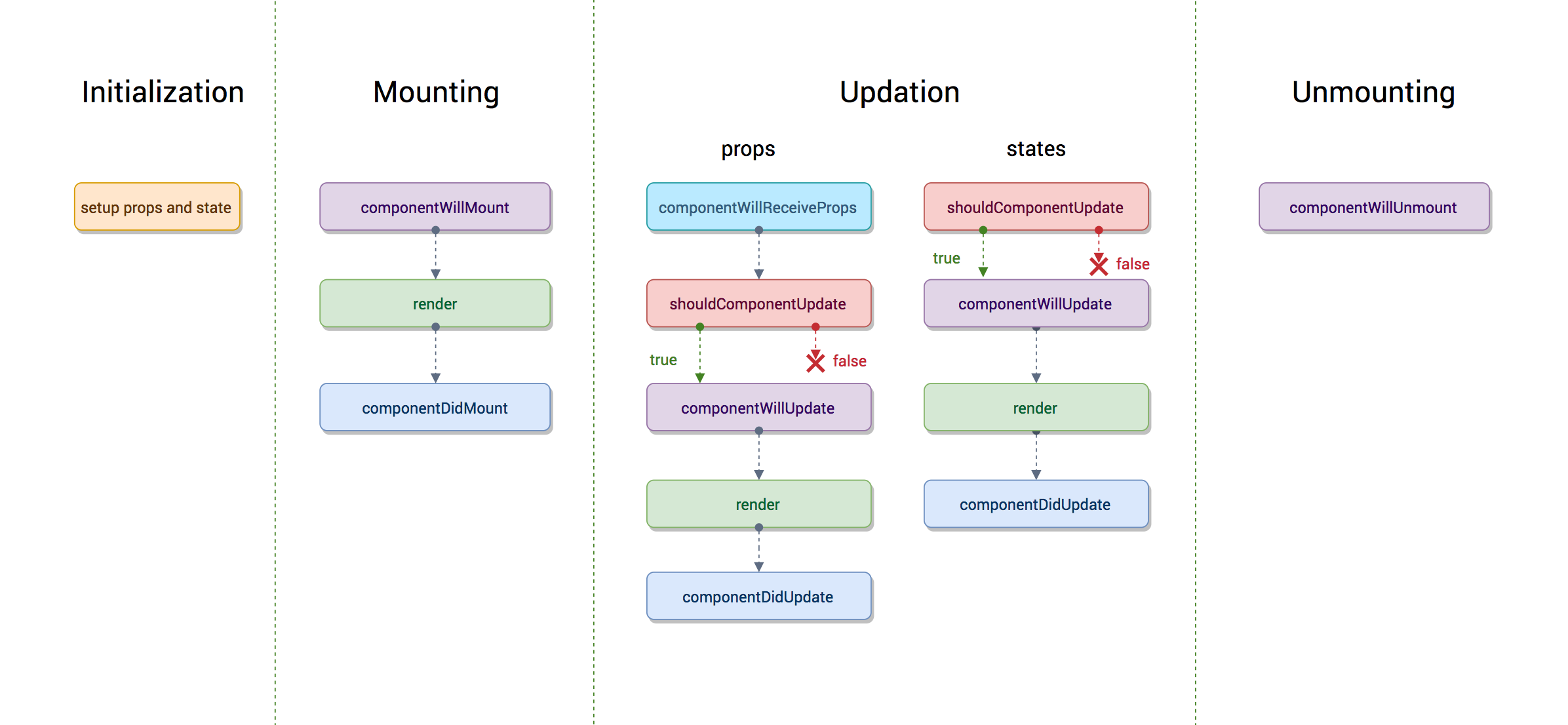
React Advanced
Optimzing Performance
- 필요할 때만 render 하여, 최적화 시키는 작업
- 즉, 불필요한 render를 줄이는 방법
Reconciliation (조정)
- 대전제 -> 훨씬 효율적으로 Rerender 컨트롤 가능
- 랜더 전후의 일치 여부를 판단하는 규칙
- 서로 다른 타입의 두 엘리먼트는 서로 다른 트리를 만들어 낸다.
- 개발자가 key prop을 통해, 여러 렌더링 사이에서 어떤 자식 엘리먼트가 변경되지 않아야 할지 표시해 줄 수 있다.
서로 다른 타입의 element를 부모로 하는 Component의 차이 (Unmount, Mount)
- 같은 컴포넌트(
<Foo />)를 render 하지만, 상위 타입이 다르기 때문에 두개는 다르다고 인식- -> 짝수와 홀수의 type이 다르기 때문에 서로 사라져서 Unmount , moount가 번갈아가면서 나타날 수 밖에 없음
- 같다면 상위 타입까지 같게 해서 제대로 표현 해줘야 함
import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
// Foo Component
class Foo extends React.Component {
// <p>Foo</p> 가 출력된 후, DidMount를 console 에 보여줌
componentDidMount() {
console.log("Foo ComponentDidMount!");
}
// <p>Foo</p> 가 없어지기 전에, WillUnmount를 console 에 보여줌
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("Foo componentWillUnmount!");
}
render() {
return <p>Foo</p>;
}
}
// App Component
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
// render되면, 1초에 한번씩 state의 count를 1씩 증가
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
// state의 count가 짝수면 div 타입의 Foo, 아니면, span 타입의 Foo 컴포넌트를 render 함
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return (
<div>
<Foo />
</div>
);
}
return (
<span>
<Foo />
</span>
);
}
}
export default App;같은 Element에서 속성(Attr) 값만 다른 경우 (-> Update)
- 같은 Dom Element인데 attribute 값만 달라지는 경우, 해당 attribute 값만 변하여 표현됨 (DOM Element가 unMount 되지 않고 update만 됨)
import './App.css';
import React from 'react';
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return (
<div className="before" title="stuff" />
<div style={{ color: 'red', fontWeight: 'bold' }} />
);
}
return (
<div className="after" title="stuff" />
<div style={{ color: 'green', fontWeight: 'bold' }} />
);
}
}
export default App;같은 Component에서 같은 prop가 다른 값을 가지는 경우(-> Update)
- 같은 Component에 다른 prop의 값을 가지는 경우, 컴포넌트가 unmount 되지 않고 component의 props 값이 업데이트 되어 rereder 됨
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
class Foo extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log("Foo ComponentDidMount!");
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("Foo componentWillUnmount!");
}
render() {
console.log("Foo render!");
return <p>Foo</p>;
}
// render 전에 실행됨
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevProps) {
console.log("Foo getDerivedStateFromProps", nextProps, prevProps);
return {};
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return <Foo name="kim" />;
}
return <Foo name="park" />;
}
}
export default App;
// Foo getDerivedStateFromProps {name: "park"} {}
// Foo render!
// Foo getDerivedStateFromProps {name: "kim"} {}
// Foo render!
// ... 반복Compenent 자체가 사라지거나 생겨 변경 되는 경우 Component 동일성 주기 (key prop)
- 기본적으로 전과 후를 비교하여, 사라지는 것은 Unmount 하고 새로 생겨나면 DidMount 함, 기존에 있었던 것은 Update만 할뿐 임
- 3개에서 2개의 컴포넌트로 줄어 들어 render 될 때,
- 이미 third가 render 되어 있고 seconde 다음으로 끝나는 명령을 수행 할때 차이를 인식하고 그때 기존의 third에 대한 willUnmount 후 Unmount가 발생 함
keyprop을 전달하여 Component 동일성을 주어 같게 인식하게 할 수 있음
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
class Foo extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log("Foo ComponentDidMount!");
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("Foo componentWillUnmount!");
}
render() {
console.log("Foo render!", this.props.children);
return <p>Foo</p>;
}
// render 전에 실행됨
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevProps) {
console.log("Foo getDerivedStateFromProps", nextProps, prevProps);
return {};
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return (
<ul>
<Foo>first</Foo>
<Foo>second</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
return (
<ul>
<Foo>first</Foo>
<Foo>second</Foo>
<Foo>third</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
}
// third가 있는 ul render 후, third 없는 ul render시 second 를 render 후 끝 마칠때 전과 비교하여, third가 없음을 인지하고 willUnmount 하고 Unmount를 함
export default App;- component에서 children props의 경우, 컴포넌트 시작 태그와, 끝남 태그 사이에 있는 정보를 담고 있음
- 그래서 해당 children을 기준으로 같은 컴포넌트임을 인식하지 않음 -> key prop에 id 값을 넣어 같은 컴포넌트임을 인식 시켜줌
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
// Foo Component 정의 생략 ...
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return (
<ul>
<Foo>second</Foo>
<Foo>third</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
return (
<ul>
<Foo>first</Foo>
<Foo>second</Foo>
<Foo>third</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
}
// 단순히, children 값을 기준으로 같은 컴포넌트인지 인식하지 않고, 생성 순서대로 component가 같은 것으로 봄
export default App;- first Component에 대해서만 DidMount, WillUnmount가 되어
keyprop를 통해서 컴포넌트에 대한 동일성을 부여할 수 있음 (동일성 부여하면, 새로 생성하는 것과 유지하는 것을 제어할 수 있음)
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
class Foo extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
console.log("Foo ComponentDidMount!", this.props.children);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("Foo componentWillUnmount!");
}
render() {
console.log("Foo render!", this.props.children);
return <p>Foo</p>;
}
// render 전에 실행됨
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevProps) {
console.log("Foo getDerivedStateFromProps", nextProps, prevProps);
return {};
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
componentDidMount() {
setInterval(() => {
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
}, 1000);
}
render() {
if (this.state.count % 2 === 0) {
return (
<ul>
<Foo key="2">second</Foo>
<Foo key="3">third</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
return (
<ul>
<Foo key="1">first</Foo>
<Foo key="2">second</Foo>
<Foo key="3">third</Foo>
</ul>
);
}
}
// first Component에 대해서만 DidMount, WillUnmount가 되어 key를 통해서 컴포넌트에 대한 동일성을 부여할 수 있음(동일성 부여하면, 다르게 생성하지 않음)
export default App;전달 받은 props 업데이트에 따른 Rerender 막기 (class, function component)
- state를 update하여 props를 건네는 경우 화면이 변하게 하는 props가 아닌 경우 render 낭비임 -> Update는 하지만 rerender에 를 막아야함
shouldComponentUpdate 방식 (Class Component)
shouldComponentUpdate를 활용함- setState, newProps의 경우 render하기 전에, 이전 props와 현재 받아오는 props를 비교하여 render를 할지 말지 결정 함
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
class Person extends React.Component {
// 이전 props와 현재 받아오는 props를 비교
shouldComponentUpdate(prevProps) {
// 모든 props를 가져와서 전과 비교함
for (const key in this.props) {
if (prevProps[key] !== this.props[key]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
render() {
const { name, age } = this.props;
console.log("Person render!");
return (
<div>
name : {name}, age: {age}
</div>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
text: "",
persons: [
{ id: 1, name: "Kim", age: 30 },
{ id: 2, name: "Park", age: 25 },
],
};
render() {
const { text, persons } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={text} onChange={this._change} />
<ul>
{persons.map((person) => {
return <Person {...person} key={person.id} />;
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
// state의 text만 update 함 -> state update 되는 것으로, Person 컴포넌트도 update 됨
_change = (e) => {
this.setState({
...this.state,
text: e.target.value,
});
};
}
export default App;PureComponent 방식 (Class Component)
PureComponent로 상속받아 Component를 만들면 됨- shouldComponentUpdate에서 했던 방식을 react에서는 pure component로 지원하고 있음
- 전 props와 이후 props에 대한 비교에 대한 로직이 이미 짜여져 있음
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
// PureComponent
class Person extends React.PureComponent {
// shouldComponentUpdate(prevProps) {
// for (const key in this.props) {
// if (prevProps[key] !== this.props[key]) {
// return true;
// }
// }
// return false;
// }
render() {
const { name, age } = this.props;
console.log("Person render!");
return (
<div>
name : {name}, age: {age}
</div>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
text: "",
persons: [
{ id: 1, name: "Kim", age: 30 },
{ id: 2, name: "Park", age: 25 },
],
};
render() {
const { text, persons } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={text} onChange={this._change} />
<ul>
{persons.map((person) => {
return <Person {...person} key={person.id} />;
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
_change = (e) => {
this.setState({
...this.state,
text: e.target.value,
});
};
}
export default App;props에 직접적으로 함수를 선언하면서 넣는 경우 rerender 막기 (Class Component)
- props에 직접적으로 함수를 선언하면서 넣으면, 해당 함수가 계속 생성되어 들어 가기 때문에 render를 막을 수 없음 (PureComponent 여도 못막음)
- 무조건 함수를 props로 전달하는 경우, 밖에서 함수로 선언해서 함수명으로 달아주어야 render를 막을 수 있음
import "./App.css";
import React from "react";
class Person extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
const { name, age } = this.props;
console.log("Person render!");
return (
<div>
name : {name}, age: {age}
</div>
);
}
}
class App extends React.Component {
state = {
text: "",
persons: [
{ id: 1, name: "Kim", age: 30 },
{ id: 2, name: "Park", age: 25 },
],
};
render() {
const { text, persons } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={text} onChange={this._change} />
<ul>
{persons.map((person) => {
// 직접적으로 props에 함수 선언으로 넣으면 -> render 못 막음
// return <Person {...person} key={person.id} onClick={() => {}} />;
return (
<Person
{...person}
key={person.id}
onClick={this.toPersonClick}
/>
);
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
}
_change = (e) => {
this.setState({
...this.state,
text: e.target.value,
});
};
toPersonClick = () => {};
}
export default App;Function Component render 막기 (React.memo())
React.memo()로 해당 컴포넌트 매개변수, body부분 묶어주기- class component의 PureComponent 처럼 shouldComponentUpdate 역할을 해줌
- 단, Arrow Funciton 표현을 통해서 component를 만들어야 함
React.useCallback()으로 함수 생성 제한 두기- function component에서는 function 키워드로 작성한 함수를 props로 전달하는 경우, 항상 새 함수로 인식하고 생성하여 props로 전달 하기 때문에 다르게 인지 하여 rerender 시킴
- useCallback 에 dependency 없이 사용함으로서 최초 render 시에만 함수를 생성하고, update하지 않음
- 단, Arrow Funciton 표현을 통해서 함수를 만들어야 함
import "./App.css";
import React, { useState } from "react";
// React.memo
const Person = React.memo(({ name, age }) => {
console.log("Person render!");
return (
<div>
name : {name}, age: {age}
</div>
);
});
function App() {
const [state, setState] = useState({
text: "",
persons: [
{ id: 1, name: "Kim", age: 30 },
{ id: 2, name: "Park", age: 25 },
],
});
// useCallback 에 dependency 없이 사용함으로서
// 최초 render 시에만 함수를 생성하고, update하지 않음 (props로 전달될 때 계속 전달되면 함수는 새로운 것이라고 인식하기 때문)
const toPersonClick = React.useCallback(() => {}, []);
const { text, persons } = state;
return (
<div>
<input type="text" value={text} onChange={change} />
<ul>
{persons.map((person) => {
return <Person {...person} key={person.id} onClick={toPersonClick} />;
})}
</ul>
</div>
);
function change(e) {
setState({
...state,
text: e.target.value,
});
}
// function toPersonClick () {}
// state 변하면 rerender 되서 함수도 rereder 됨으로 props로 전달할때 마다 Person Component가 rerender 됨
}
export default App;'Dev > React' 카테고리의 다른 글
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- 기능추가
- React
- NomadCoder
- Git
- TypeScirpt
- 그림판 만들기
- 바닐라js
- object
- github
- css
- project
- Python
- nrc
- html
- Django
- hooks
- nodejs
- async
- RUBY
- JavaScript
- 오버라이딩
- 트위터 클론
- redux-toolkit
- 생활코딩
- 드림코딩
- instagram CSS
- todolist
- Class
- Firebase
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
글 보관함
